How airlines spoil fuel in order to keep pilots off their payroll
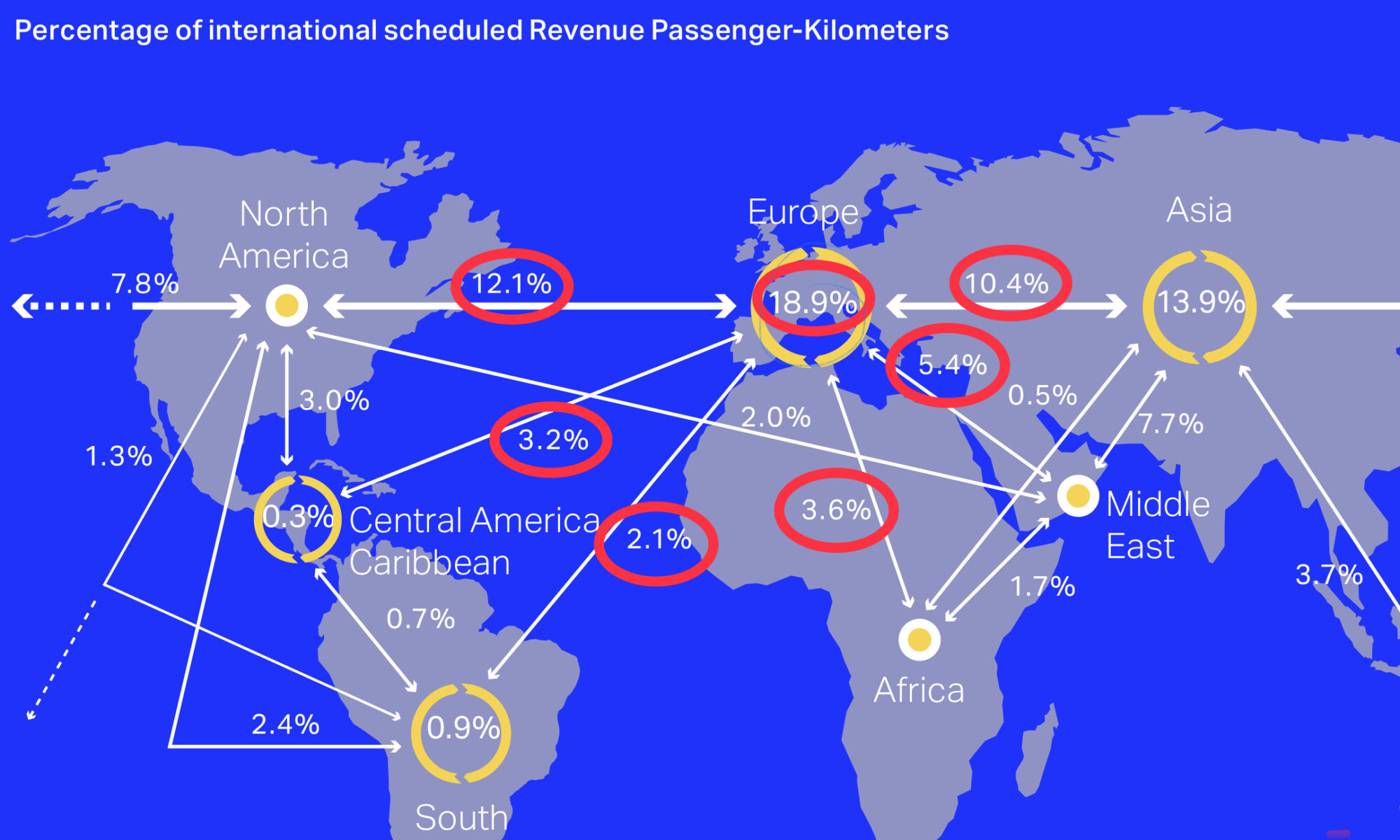
 Flights must be manned with 2 pilots. However, longer intercontinental flights must be manned with 3 or 4 pilots, because legal work and rest times regulations require pilots to have inflight-rest periods.
Flights must be manned with 2 pilots. However, longer intercontinental flights must be manned with 3 or 4 pilots, because legal work and rest times regulations require pilots to have inflight-rest periods.
Many of such flights are just beyond these regulatory limits. Due to the low price for fuel, airlines prefer to fly these flights with maximum speed instead of employing another copilot.
5% to 10%, 3-15 tons, more fuel is regularly burned for such purposes. This practice is frequently used and increases fuel consumption per flight significantly. The lower the costs for fuel, the more likely, an airline will prefer to fly fuel-spoiling fast.

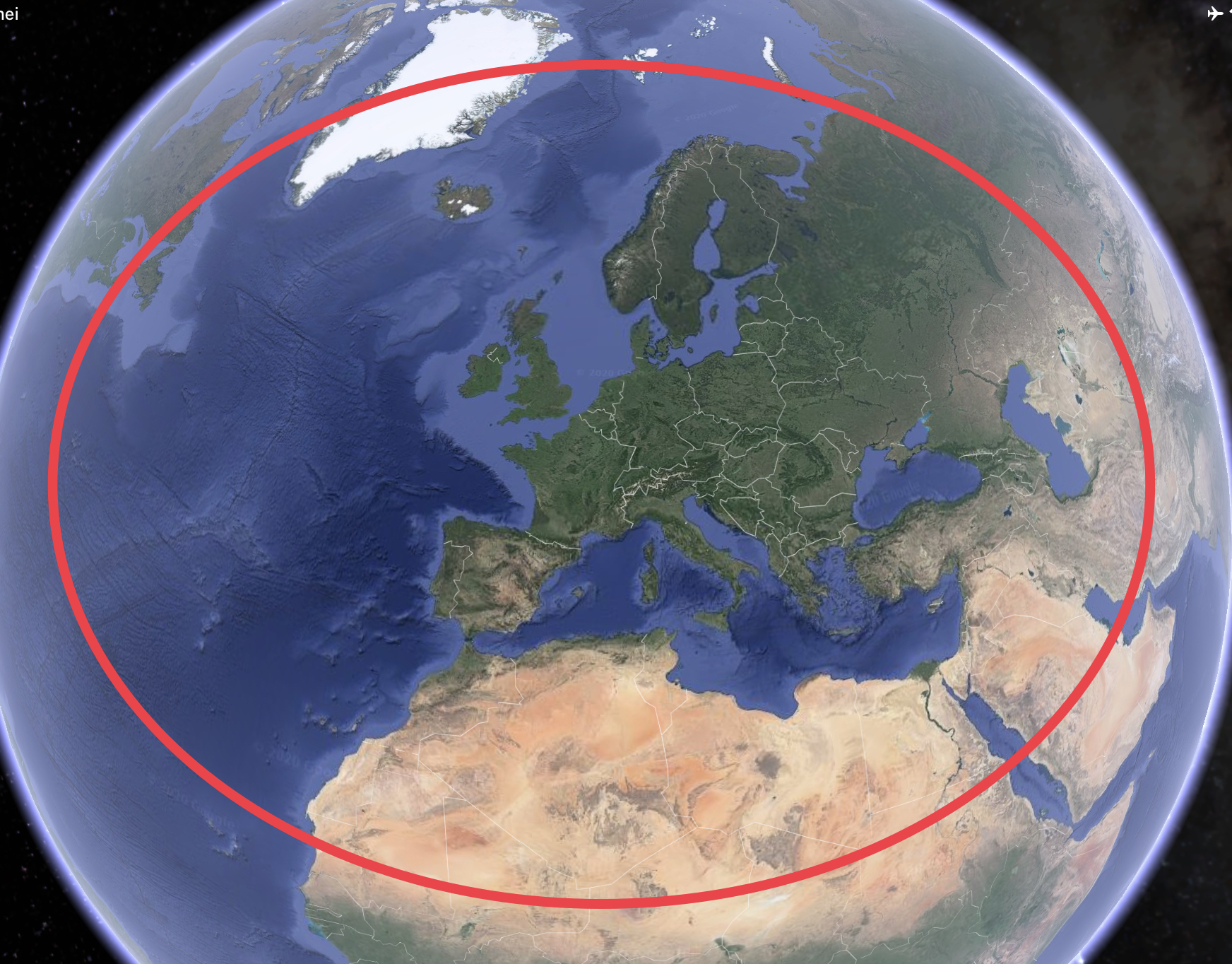 CO2 emission rules for flights outside EU ETS airspace must stop at a certain (great-circle) distance, e.g. beyond 5,000 km. This “stop the clock” policy avoids unfair competition from flights with intermediate stops outside the EU ETS. Otherwise, fuel efficient direct flights get unfair competition from less fuel efficient flights with intermediate stops.
CO2 emission rules for flights outside EU ETS airspace must stop at a certain (great-circle) distance, e.g. beyond 5,000 km. This “stop the clock” policy avoids unfair competition from flights with intermediate stops outside the EU ETS. Otherwise, fuel efficient direct flights get unfair competition from less fuel efficient flights with intermediate stops.  Aircrafts are designed around an airline’s business plan. Designers optimise an aircraft’s fuselage, it’s wings and engines to fly with a specific speed to gain an airline the highest profits.
Aircrafts are designed around an airline’s business plan. Designers optimise an aircraft’s fuselage, it’s wings and engines to fly with a specific speed to gain an airline the highest profits.  Flights must be manned with 2 pilots. However, longer intercontinental flights must be manned with 3 or 4 pilots, because legal work and rest times regulations require pilots to have inflight-rest periods.
Flights must be manned with 2 pilots. However, longer intercontinental flights must be manned with 3 or 4 pilots, because legal work and rest times regulations require pilots to have inflight-rest periods.